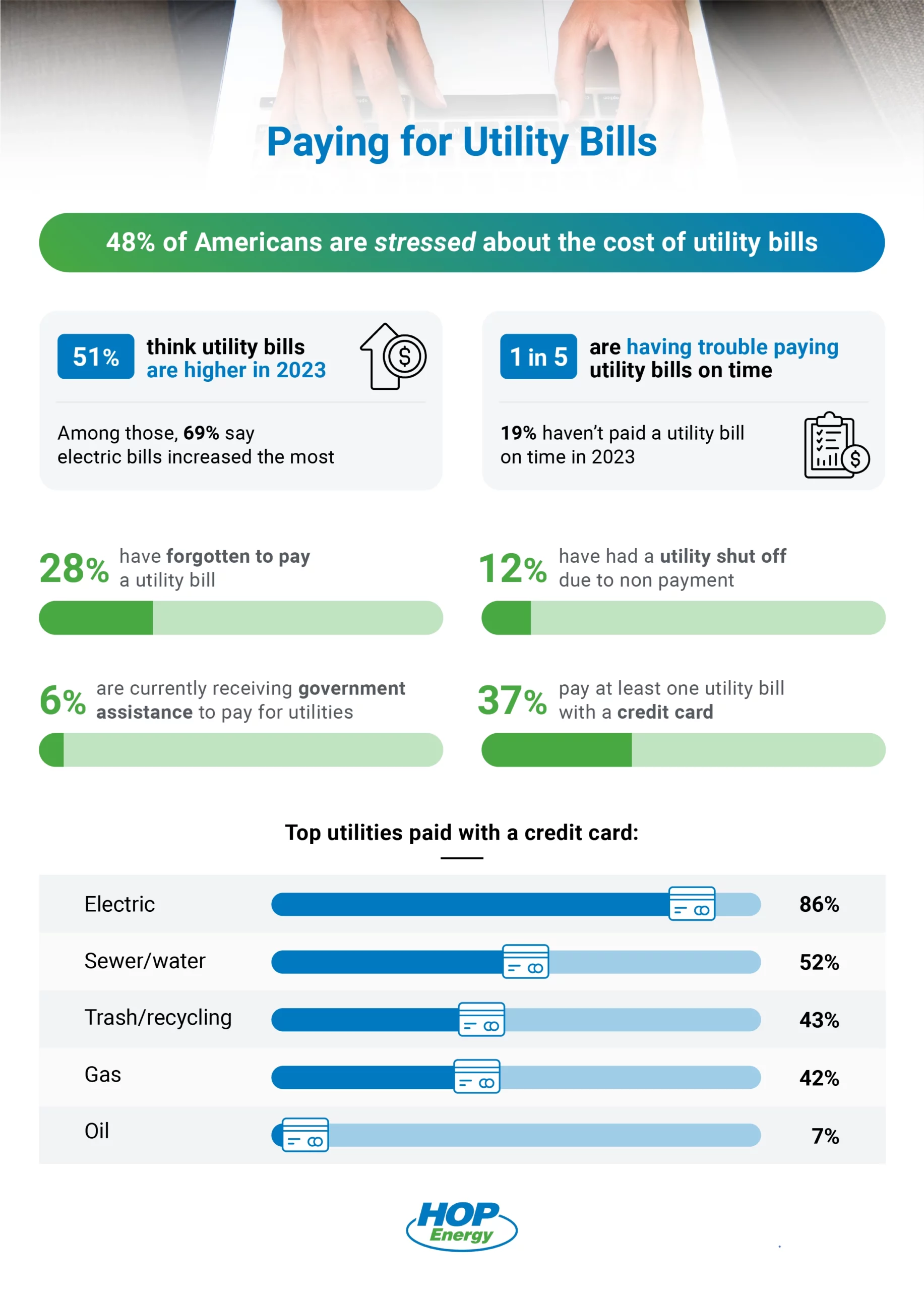
Managing your home heating costs can be a daunting task, especially when faced with unpredictable weather and fluctuating oil prices. At HOP Energy, we understand the challenges that come with budgeting for heating expenses, which is why we offer our innovative Budget Plans. Our plans are designed to provide you with the stability and peace of mind you need, allowing you to enjoy a warm home without financial stress.
Table of Contents
What Are HOP Energy Budget Plans?
HOP Energy Budget Plans are a smart, flexible way to manage your heating expenses throughout the year. Instead of paying large sums during the peak heating season, our plans spread your heating costs evenly over 12 months. This approach allows you to maintain a consistent monthly budget, making it easier to plan your finances and avoid surprises.
Benefits of HOP Energy Budget Plans
Imagine a winter without the worry of skyrocketing heating bills. With HOP Energy Budget Plans, this can be your reality. Our plans offer you the benefit of predictable monthly payments, allowing you to focus on enjoying the warmth and comfort of your home. No more scrambling to cover unexpected expenses—just a simple, manageable plan tailored to your needs.
But the benefits don’t stop there. By enrolling in our Budget Plan, you gain access to our dedicated customer support team, ready to assist you with any questions or concerns. We’re committed to providing you with a hassle-free experience, ensuring that your heating needs are met efficiently and effectively.
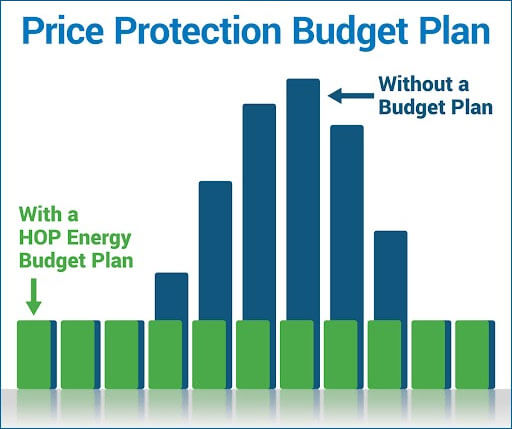
How Does It Work?
Getting started with a HOP Energy Budget Plan is easy. We calculate your estimated annual heating costs based on your previous usage and current market rates. This total is then divided into equal monthly payments, allowing you to budget with confidence. As the year progresses, we monitor your usage and make adjustments as needed, ensuring that your plan remains aligned with your actual consumption.
Why Choose HOP Energy?
When you choose HOP Energy, you’re choosing a partner that puts your needs first. Our Budget Plans are just one of the many ways we strive to deliver exceptional value and service to our customers. We believe that managing your home heating should be stress-free, and we’re dedicated to making that a reality.
By opting for a HOP Energy Budget Plan, you’re not only securing stable heating costs—you’re investing in peace of mind. You can rest easy knowing that your home will stay warm and comfortable all year round, without the financial burden of fluctuating bills.
Get Started Today
Don’t wait until the next cold snap to take control of your heating costs. Contact our friendly customer service team at 833-837-7690 to learn more about HOP Energy Budget Plans and how they can benefit you. Join the many homeowners who trust us to keep their homes warm and their budgets on track.
Thank you for choosing HOP Energy. We’re proud to be your trusted heating partner, helping you enjoy a cozy, worry-free home.